Determine the standard entropy changes for the following reactions at 25° C:
(a) H2 (g) + CuO(s) → Cu(s) + H2O(g)
(b) 2 Al (s) + 3 ZnO (s) → Al2O3 (s) + 3 Zn (s)
(c) CH4 (g) + 2 O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (l)
Standard entropy values:
| Substance | Standard Entropy (S°) (J/(K·mol)) |
| Cu (s) | 33.3 |
| CuO (s) | 43.5 |
| H2(g) | 131 |
| H2O(g) | 188.7 |
| Al(s) | 28.33 |
| ZnO(s) | 43.9 |
| Zn(s) | 41.6 |
| Al2O3(s) | 50.99 |
| CH4(g) | 186.2 |
| O2(g) | 205.0 |
| CO2(g) | 213.6 |
| H2O(l) | 69.9 |
Interpretation: The standard entropy changes for a reaction, ∆S°rxn, is given by the difference in standard entropies between products and reactants. Thus, it reflects the change in disorder or randomness during the reaction.
We can calculate Standard entropy changes by using the following formula:
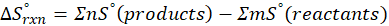
Where, ∆S°rxn = Standard entropy change for the reaction
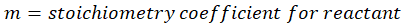
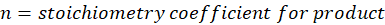

Solution:
(a) H2 (g) + CuO(s) → Cu(s) + H2O(g)
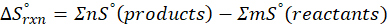
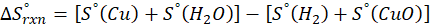
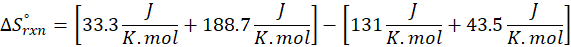
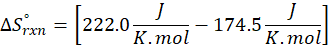
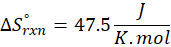
Therefore, the entropy increases by 47.5 J/K.mol for the reaction H2 (g) + CuO(s) → Cu(s) + H2O(g)
(b) 2 Al (s) + 3 ZnO (s) → Al2O3 (s) + 3 Zn (s)
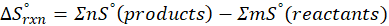
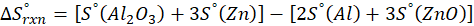

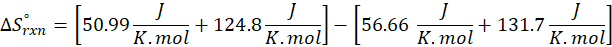
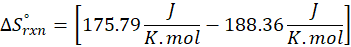
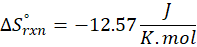
Therefore, the entropy decreases by – 12.57 J/K.mol for the reaction 2 Al (s) + 3 ZnO (s) → Al2O3 (s) + 3 Zn (s).
(c) CH4 (g) + 2 O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (l)
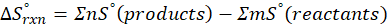
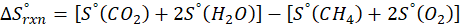
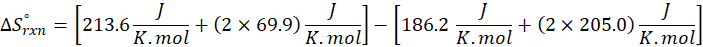
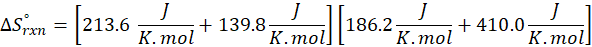
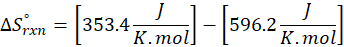
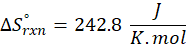
Therefore, the entropy increases by 242.8 J/K.mol for the reaction CH4 (g) + 2 O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (l).
